Data Science is a rapidly growing field that uses scientific methods, algorithms, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data. As the field evolves, it is important to have a practical roadmap to guide aspiring data scientists on how to start and progress in their careers. In this blog, we will outline a practical data science roadmap for beginners and intermediate-level data scientists.
1. Programming and Statistics

Programming and statistics form the foundation of data science. It is essential to have a good grasp of programming languages such as Python, R, and SQL. Understanding statistics is also critical in data science, as it provides a framework for understanding data and interpreting results. Linear algebra and calculus are also essential in data science, as they are used in machine learning algorithms.
2. Data Collection and Preparation
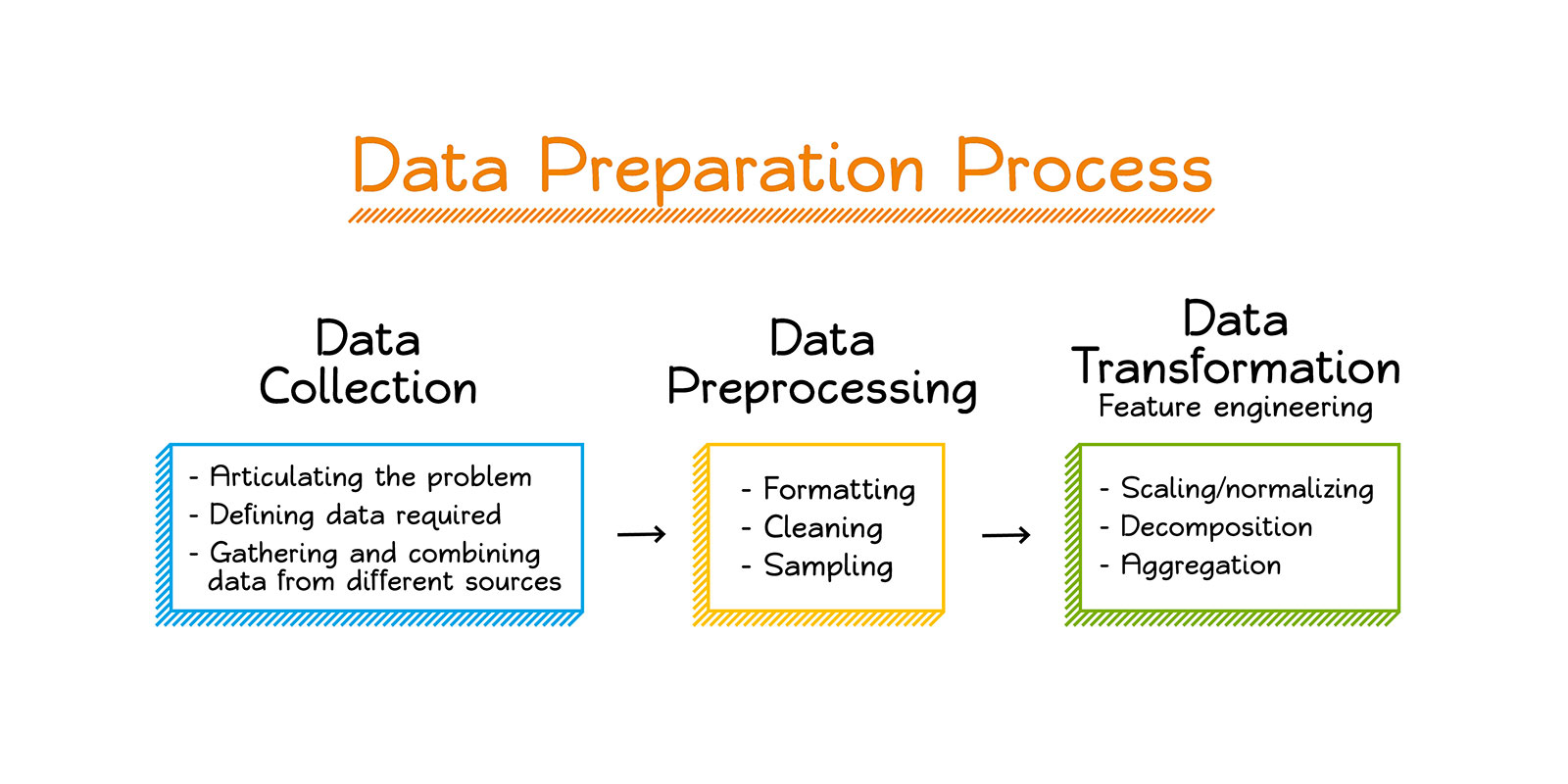
Data collection and preparation involve gathering and preparing data for analysis. This includes data cleaning, data wrangling, and data exploration. Understanding data collection methods such as web scraping and API calls is also crucial. Learning how to use data manipulation tools such as pandas, NumPy, and SQL is also important.
3. Data Visualization
Data visualization is a key aspect of data science. Visualization is used to communicate insights and findings to stakeholders. It is important to have a good understanding of visualization tools such as Matplotlib, Seaborn, and Plotly. Learning how to create visualizations that are easy to interpret is critical.
4. Machine Learning

Machine learning is the core of data science. It involves using algorithms to learn patterns in data and make predictions. It is important to understand the different types of machine learning such as supervised and unsupervised learning, and how to use algorithms such as linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, random forests, and neural networks. Learning how to evaluate machine learning models is also critical.
5. Deep Learning

Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that involves neural networks with many layers. Deep learning is used in applications such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing. Understanding how to build and train deep learning models using frameworks such as TensorFlow, Keras, and PyTorch is essential.
6. Big Data Technologies

Big Data technologies are used to handle large datasets that cannot be processed by traditional tools. Understanding distributed computing frameworks such as Hadoop and Spark, and cloud computing platforms such as AWS and Azure is critical. Learning how to use tools such as Hive, Pig, and MapReduce is also important.
7. Data Engineering
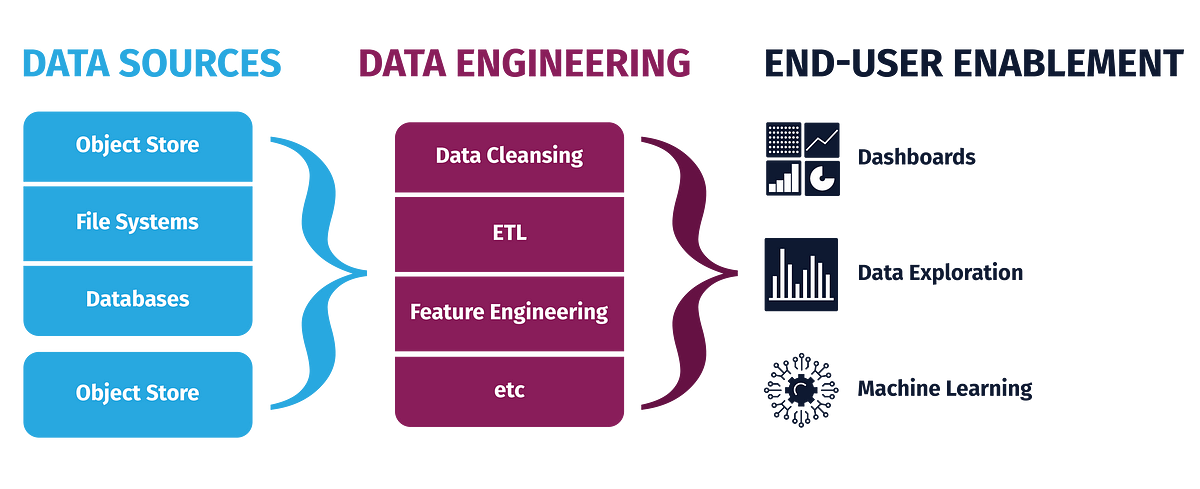
Data engineering involves designing and building data pipelines that collect, process, and store data. It is important to understand how to work with databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. Understanding how to use data warehousing tools such as Amazon Redshift, and ETL tools such as Apache NiFi is also critical.
8. Deployment and Production
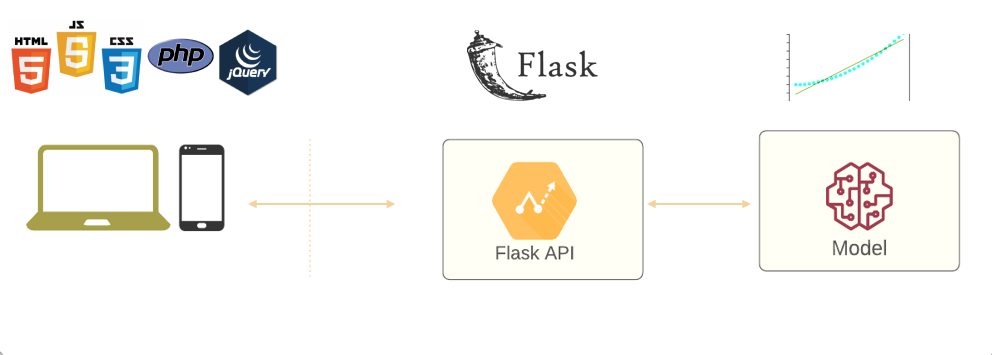
Deploying and productionizing models is a critical aspect of data science. It is important to understand how to deploy models to production environments such as web servers and mobile devices. Learning how to use deployment tools such as Flask, Docker, and Kubernetes is also important.
Conclusion
The practical data science roadmap outlined in this blog provides a guide for beginners and intermediate-level data scientists on how to start and progress in their careers. By mastering programming, statistics, data collection and preparation, data visualization, machine learning, deep learning, big data technologies, data engineering, and deployment and production, data scientists can become proficient in the field and make a meaningful impact on their organizations.